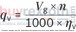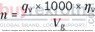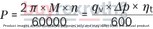***Disclaimer: The following summary contains information gathered from various sources such as product descriptions, technical specifications and catalogs. While efforts have been made to provide accurate details, inaccuracies may occur. It is advised to verify all information by contacting Bosch Rexroth directly.***
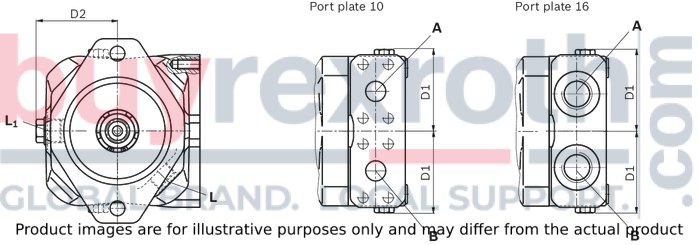
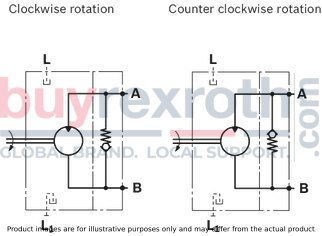
The Bosch Rexroth AL A10F M 45 /52W-VWC66N007 (R902505555) is a medium pressure hydraulic motor designed for both open and closed circuit applications. This motor utilizes well-tried A rotary group technology, ensuring reliability and efficiency in operation. It is approved for high-speed uses, which makes it suitable for a range of standard applications that demand quick and responsive power. The robust design of this motor contributes to its long service life and high power density, providing a compact yet powerful solution for hydraulic systems.
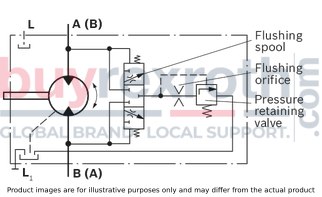
One of the key features of the AL A10F M 45 /52W-VWC66N007 is its low operating noise, which enhances the working environment by reducing acoustic stress. This feature is particularly beneficial in settings where noise reduction is crucial. Additionally, it offers optional integrated anticavitation valves, such as those required for fan drives, which prevent damage caused by cavitation and ensure stable performance under varying load conditions.
The swashplate design of this Bosch Rexroth motor allows for fine-tuned control over speed and torque output. Furthermore, there is an option to integrate a speed sensor with this model, enabling precise monitoring of motor speeds—a critical requirement in many automated processes where exact motion control is necessary.
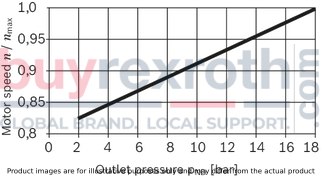
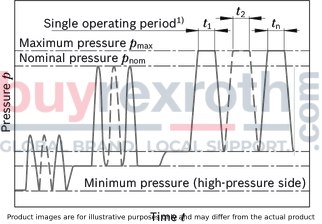
With nominal pressure ratings bar and maximum pressure ratings bar, the AL A10F M 45 /52W-VWC66N007 motor is built to withstand rigorous operational demands while maintaining efficiency and durability. Its well-engineered structure ensures that it can handle the pressures of everyday use in a variety of standard applications without compromising on performance or longevity.
$2,521.00 USD
Availability: 20 In Stock
Note: Sales tax, shipping, and applicable tariffs will be calculated at checkout. Available for immediate shipmentQty: Delivered as early as September 2, 2025 when ordered in