***Disclaimer: The following summary contains information gathered from various sources such as product descriptions, technical specifications and catalogs. While efforts have been made to provide accurate details, inaccuracies may occur. It is advised to verify all information by contacting Bosch Rexroth directly.***
The Bosch Rexroth A2FE63/61W-VAL100 (R902205887) is a high-pressure motor designed for seamless integration into mechanical gearboxes. This motor stands out due to its space-saving construction, featuring a recessed mounting flange that allows for compact installation. It has been engineered to slide easily into the mechanical gearbox, simplifying the installation process. The A2FE63/61W-VAL100 boasts a high power density and an exceptional total efficiency, ensuring optimal performance even under demanding conditions.
With its high starting efficiency, this motor is well-suited for applications requiring reliable operation from the outset. Users have the option to include an integrated pressure relief valve, enhancing the safety and functionality of the system. Additionally, there is the possibility to mount additional valves such as counterbalance valve BVDBVE, flushing and boost pressure valve, which can further tailor the motor to specific application needs.
The bent-axis design of this model is pivotal for its efficient operation and suitability in both open and closed circuit systems. The A2FE63/61W-VAL100 operates at a nominal pressure of up to 400 bar and can withstand a maximum pressure of up to 450 bar, making it robust enough for use in environments where high pressures are commonplace.
Overall, this Bosch Rexroth hydraulic motor is crafted with precision to offer reliable performance in various applications that require integration with mechanical gearboxes while maintaining space efficiency and adaptability through optional features.
$5,483.00 USD
More are expected on August 20, 2026
Status: This product is temporarily out of stock.
Qty: Delivered as early as August 20, 2026 when ordered in
This product is eligible for factory repair.
Space-saving construction due to recessed mounting flange Easy to install, simply slide into the mechanical gearbox High power density Very high total efficiency High starting efficiency Optional with integrated pressure relief valve Optional with mounted addifitonal valve: counterbalance valve (BVD/BVE), flushing and boost-pressure valve Bent-axis design


| 1) | Please contact us. |
| 2) | Specify ordering code of counterbalance valve according to data sheet 95522 (BVD) respectively data sheet 95525 (BVE) separately. |
| 3) | Specify ordering code of sensor according to data sheet 95133 (DSA) respectively data sheet 95135 (HDD) separately. |
Table of values
|
Size |
28 | 32 | 107 | 125 | 160 | 180 | 250 | 355 | |||
|
Displacement |
Vg |
cm³ |
28.1 | 32 | 106.7 | 125 | 160.4 | 180 | 250 | 355 | |
|
Nominal pressure |
pnom |
bar |
400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 350 | 350 | |
|
Maximum pressure |
pmax |
bar |
450 | 450 | 450 | 450 | 450 | 450 | 400 | 400 | |
|
Maximum speed |
nnom 1) |
rpm |
6300 | 6300 | 4000 | 4000 | 3600 | 3600 | 2700 | 2240 | |
|
nmax 2) |
rpm |
6900 | 6900 | 4400 | 4400 | 4000 | 4000 | ||||
|
Inlet flow 3) |
at nnom |
qV |
l/min |
177 | 202 | 427 | 500 | 577 | 648 | 675 | 795 |
|
Torque 4) |
at pnom |
M |
Nm |
179 | 204 | 679 | 796 | 1021 | 1146 | 1393 | 1978 |
|
Rotary stiffness |
c |
kNm/rad |
2.93 | 3.12 | 11.2 | 11.9 | 17.4 | 18.2 | 73.1 | 96.1 | |
|
Moment of inertia for rotary group |
JTW |
kg·m² |
0.0012 | 0.0012 | 0.0116 | 0.0116 | 0.022 | 0.022 | 0.061 | 0.102 | |
|
Maximum angular acceleration |
ɑ |
rad/s² |
6500 | 6500 | 4500 | 4500 | 3500 | 3500 | 10000 | 8300 | |
|
Case volume |
V |
l |
0.2 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 2.5 | 3.5 | |
|
Weight (approx.) |
m |
kg |
10.5 | 10.5 | 34 | 36 | 47 | 48 | 82 | 110 | |
| 1) |
These values are valid at: - for the optimum viscosity range from vopt = 36 to 16 mm2/s - with hydraulic fluid based on mineral oils |
| 2) | Intermittent maximum speed: overspeed for unload and overhauling processest, t < 5 s and Δp < 150 bar |
| 3) | Restriction of input flow with counterbalance valve |
| 4) | Torque without radial force, with radial force see table "Permissible radial and axial forces of the drive shafts" |
Note
The values in the table are theoretical values, without consideration of efficiencies and tolerances. The values are rounded. Exceeding the maximum or falling below the minimum permissible values can lead to a loss of function, a reduction in operational service life or total destruction of the axial piston unit. Other permissible limit values, such as speed variation, reduced angular acceleration as a function of the frequency and the permissible angular acceleration at start (lower than the maximum angular acceleration) can be found in data sheet 90261.Speed range
No limit to minimum speed nmin. If uniformity of motion is required, speed nmin must not be less than 50 rpm.
|
Determining the operating characteristics |
||
|
Inlet flow |
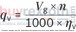
|
[l/min] |
|
Rotational speed |
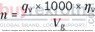
|
[rpm] |
|
Torque |

|
[Nm] |
|
Power |
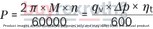
|
[kW] |
|
Key |
|
|
Vg |
Displacement per revolution [cm3] |
|
Δp |
Differential pressure [bar] |
|
n |
Rotational speed [rpm] |
|
ηv |
Volumetric efficiency |
|
ηhm |
Hydraulic-mechanical efficiency |
|
ηt |
Total efficiency (ηt = ηv • ηhm) |
Hydraulic fluids
The axial piston unit is designed for operation with mineral oil HLP according to DIN 51524.
Application instructions and requirements for hydraulic fluids should be taken from the following data sheets before the start of project planning:
90220: Hydraulic fluids based on mineral oils and related hydrocarbons 90221: Environmentally acceptable hydraulic fluids 90222: Fire-resistant, water-free hydraulic fluids (HFDR, HFDU) 90223: Fire-resistan, water-containing hydraulic fluids (HFAE, HFAS, HFB, HFC) 90225: Restricted technical data for operation with fire-resistant hydraulic fluidsViscosity and temperature of hydraulic fluids
|
|
Viscosity |
Shaft |
Temperature1) |
Comment |
|
Cold start |
νmax ≤ 1600 mm²/s |
NBR2) |
ϑSt ≥ -40 °C |
t ≤ 3 min, without load (p ≤ 50 bar), n ≤ 1000 rpm, |
|
FKM |
ϑSt ≥ -25 °C |
|||
|
Warm-up phase |
ν = 400 … 1600 mm²/s |
|
t ≤ 15 min, p ≤ 0.7 • pnom and n ≤ 0.5 • nnom |
|
|
Continuous operation |
ν = 10 … 400 mm²/s3) |
NBR2) |
ϑ ≤ +78 °C |
measured at port T |
|
FKM |
ϑ ≤ +103 °C |
|||
|
νopt = 16 … 36 mm²/s |
range of optimum operating viscosity and efficiency |
|||
|
Short-term operation |
νmin = 7 … 10 mm²/s |
NBR2) |
ϑ ≤ +78 °C |
t ≤ 3 min, p ≤ 0.3 • pnom measured at port T |
|
FKM |
ϑ ≤ +103 °C |
| 1) | If the specified temperatures cannot be maintained due to extreme operating parameters, please contact us. |
| 2) | Special version, please contact us. |
| 3) | Equates e.g. with the VG 46 a temperature range of +5 °C to +85 °C (see selection diagram) |
Note
To reduce high temperature of the hydraulic fluid in the axial piston unit we recommend the use of a flushing and boost pressure valve (see chapter Extended functions and versions).
Selection of hydraulic fluid
Bosch Rexroth evaluates hydraulic fluids on the basis of the Fluid Rating according to the technical data sheet 90235.
Hydraulic fluids with positive evaluation in the Fluid Rating are provided in the following technical data sheet:
90245: Bosch Rexroth Fluid Rating List for Rexroth hydraulic components (pumps and motors)The hydraulic fluid should be selected so that the operating viscosity in the operating temperature range is within the optimum range (νopt; see selection diagram).
Selection diagram
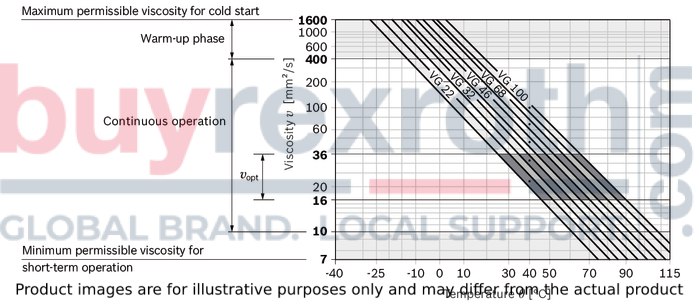
Filtration of the hydraulic fluid
Finer filtration improves the cleanliness level of the hydraulic fluid, which increases the service life of the axial piston unit.
A cleanliness level of at least 20/18/15 is to be maintained according to ISO 4406.
At a hydraulic fluid viscosity of less than 10 mm²/s (e.g. due to high temperatures in short-term operation) at the drain port, a cleanliness level of at least 19/17/14 according to ISO 4406 is required.
For example, the viscosity is 10 mm²/s at:
HLP 32 a temperature of 73°C HLP 46 a temperature of 85°COperating pressure range
|
Pressure at working port A or B (high-pressure side) |
Definition |
||
|
Nominal pressure |
pnom |
see table of values |
The nominal pressure corresponds to the maximum design pressure. |
|
Maximum pressure |
pmax |
see table of values |
The maximum pressure corresponds to the maximum operating pressure within the single operating period. The sum of the single operating periods must not exceed the total operating period. |
|
Single operating period |
10 s |
||
|
Total operating period |
300 h |
||
|
Minimum pressure |
pHP min |
25 bar |
Minimum pressure on high-pressure side (port A or B) required to prevent damage to the axial piston unit. |
|
Minimum pressure at inlet (pump operating mode) |
pE min |
see diagram |
To prevent damage to the axial piston motor in pump mode (change of high-pressure side with unchanged direction of rotation, e.g. when braking),a minimum pressure must be guaranteed at the working port (inlet). The minimum pressure depends on the rotational speed and displacement of the axial piston unit. |
|
Total pressure |
pSu |
700 bar |
The summation pressure is the sum of the pressures at both work ports (A and B). |
|
Rate of pressure change |
Definition |
||
|
with integrated pressure relief valve |
RA max |
9000 bar/s |
Maximum permissible rate of pressure build-up and reduction during a pressure change over the entire pressure range. |
|
without pressure relief valve |
RA max |
16000 bar/s |
|
|
Case pressure at port T |
Definition |
||
|
Continuous differential pressure |
ΔpT cont |
2 bar |
Maximum averaged differential pressure at the shaft seal (case to ambient) |
|
Pressure peaks |
pT peak |
10 bar |
t < 0.1 s |
Note
Working pressure range valid when using hydraulic fluids based on mineral oils. Values for other hydraulic fluids, please contact us.Minimum pressure at inlet (pump operating mode)
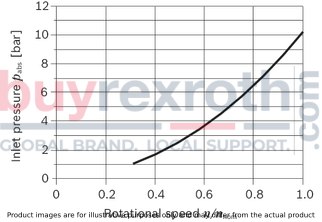
This diagram is only valid for the optimum viscosity range of vopt = 16 to 36 mm2/sec..
If the above mentioned conditions cannot be ensured, please contact us.
Pressure definition
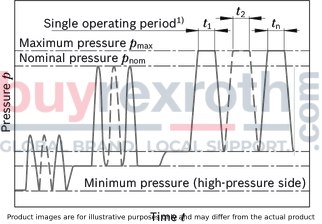
| 1) | Total operating period = t1 + t2 + ... + tn |
Rate of pressure change

Maximum differential pressure at the shaft seal
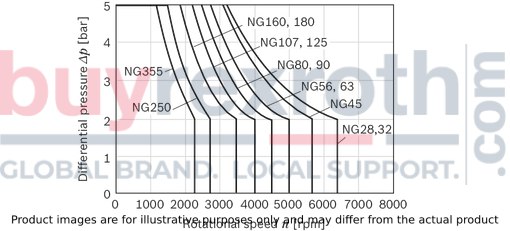
Note
The service life of the shaft seal is influenced by the speed of the axial piston unit and the case pressure. The service life decreases with an increase of the mean differential pressure between the case and the ambient pressure and with a higher frequency of pressure spikes. The case pressure must be equal to or higher than the ambient pressure.Direction of flow
|
Direction of rotation, viewed on drive shaft |
|
|
clockwise |
counter-clockwise |
|
A to B |
B to A |
Permissible radial and axial forces of the drive shaft
|
Size |
|||
|
Drive shaft |
Code |
||
|
⌀ |
|||
|
Maximum radial force |

|
Fq max |
|
|
a |
|||
|
Permitted torque at Fq max |
Tq max |
||
|
Permitted differential pressure at Fq max |
Δpq max |
||
|
Maximum axial force, when standstill or in non-pressurized conditions |

|
+ Fax max |
|
|
- Fax max |
|||
|
Maximum axial force, per bar operating pressure |
+ Fax max |
||
General instructions
The values given are maximum values and do not apply to continuous operation. The axial force in direction −Fax is to be avoided as the service life of the bearing is reduced. Special requirements apply in the case of belt drives. Please contact us.Notes for sizes 250 ... 355:
In case of radial forces limited performance data is valid. Please contact us. In case of axial forces during operation of the unit please contact us.Effect of radial force Fq on the service life of bearings
By selecting a suitable direction of radial force Fq the load on the bearings caused by the internal rotary group forces can be reduced, thus optimizing the service life of the bearings. Recommended position of mating gear is dependent on direction of rotation. Examples:
Toothed gear drive, size 28 … 180

Toothed gear drive, size 250 … 355
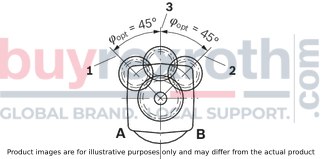
|
1 |
Direction of rotation "counter-clockwise", pressure at port B |
|
2 |
Direction of rotation "clockwise", pressure at port A |
|
3 |
Direction of rotation "bidirectional" |
Long-Life bearing
Sizes 250 and 355
For long service life and use with HF hydraulic fluids. Identical external dimensions as version with standard bearings. Subsequent conversion to long-life bearings is possible.
Size 28 ... 180
Port plate 10

| 1) | To shaft collar |
| 2) | The O-ring is not included in the delivery contents. |
|
Size |
D1 |
D2 |
D3 |
D4 |
D5 |
D7 |
D8 |
D9 |
D10 |
D11 |
D14 |
D15 |
D16 |
D17 |
D18 |
D21 |
D27 |
D28 |
D29 |
D31 |
D32 |
D33 |
D34 |
D36 |
D37 |
D40 |
D41 |
D42 |
D46 |
O-Ring |
|
|
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
|
| 28 | 135 |
0 - 0.025 |
94 | 114 | 106 | 71 | 188 | 16 | 15 | 88.8 | 87.1 | 91 | 94 | 10 | 27 | 45 | 95 | 154 | 160 | 14 | 5.2 | 106 | 115 | 40 | 42 | 13 | 18.2 | 40.5 | 13 | 59 | Ø126 × 4 |
| 32 | 135 |
0 - 0.025 |
94 | 114 | 106 | 71 | 188 | 16 | 15 | 88.8 | 87.1 | 91 | 94 | 10 | 27 | 45 | 95 | 154 | 160 | 14 | 5.2 | 106 | 115 | 40 | 42 | 13 | 18.2 | 40.5 | 13 | 59 | Ø126 × 4 |
| 107 | 200 |
0 - 0.029 |
152.3 | 178 | 157 | 103 | 286 | 20 | 15 | 122.8 | 119 | 136 | 143 | 16 | 41 | 58 | 135 | 232 | 250 | 22 | 5.2 | 150 | 194 | 70 | 40 | 0 | 31.8 | 66.7 | 32 | 99 | Ø192 × 4 |
| 125 | 200 |
0 - 0.029 |
152.3 | 178 | 157 | 103 | 286 | 20 | 15 | 122.8 | 119 | 136 | 143 | 16 | 41 | 58 | 135 | 232 | 250 | 22 | 5.2 | 150 | 194 | 70 | 40 | 0 | 31.8 | 66.7 | 32 | 99 | Ø192 × 4 |
| 160 | 200 |
0 - 0.029 |
171.6 | 206 | 185 | 104 | 286 | 20 | 15 | 122.8 | 119.3 | 149 | 169 | 12 | 47 | 75 | 134 | 232 | 250 | 22 | 5.2 | 180 | 194 | 70 | 42 | 0 | 31.8 | 66.7 | 32 | 99 | Ø192 × 4 |
| 180 | 200 |
0 - 0.029 |
171.6 | 206 | 185 | 104 | 286 | 20 | 15 | 122.8 | 119.3 | 149 | 169 | 12 | 47 | 75 | 134 | 232 | 250 | 22 | 5.2 | 180 | 194 | 70 | 42 | 0 | 31.8 | 66.7 | 32 | 99 | Ø192 × 4 |
Note
The dimensional drawings of the port plates with valves can be found in the chapter "Extended functions and versions".Drive shafts Z and A
| 1) | Center bore according to DIN 332 (thread according to DIN 13) |
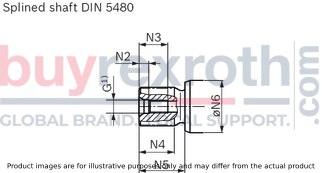
Splined shaft DIN 5480
|
NG |
Code |
Designation |
Thread G |
N2 |
N3 |
N4 |
N5 |
ØN6 |
|
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
mm |
||||
| 28 | Z | W25×1.25×18×9g | M8 × 1.25 | 6 | 19 | 28 | 43 | 35 |
| A | W30×2×14×9g | M10 × 1.5 | 7.5 | 22 | 27 | 35 | 35 | |
| 32 | A | W30×2×14×9g | M10 × 1.5 | 7.5 | 22 | 27 | 35 | 35 |
| 107 | Z | W40×2×18×9g | M12 × 1.75 | 9.5 | 28 | 37 | 45 | 50 |
| A | W45×2×21×9g | M16 × 2 | 12 | 36 | 42 | 50 | 50 | |
| 125 | A | W45×2×21×9g | M16 × 2 | 12 | 36 | 42 | 50 | 50 |
| 160 | Z | W45×2×21×9g | M16 × 2 | 12 | 36 | 42 | 50 | 60 |
| A | W50×2×24×9g | M16 × 2 | 12 | 36 | 44 | 55 | 60 | |
| 180 | A | W50×2×24×9g | M16 × 2 | 12 | 36 | 44 | 55 | 60 |
Ports
|
Size |
28 | 32 | 107 | 125 | 160 | 180 | ||
|
A, B |
Working port |
Size |
1/2 in | 1 1/4 in | ||||
|
Standard |
Dimensions according to SAE J518 | |||||||
|
Fastening thread 1) |
M8 × 1,25; 15 mm deep | M14 × 2; 19 mm deep | ||||||
|
State on delivery |
With protective cover (must be connected) | |||||||
|
T1 |
Drain port |
Size |
M16 × 1,5; 12 mm deep | M18 × 1,5; 12 mm deep | M22 × 1,5; 14 mm deep | |||
|
Standard 2) |
DIN 3852 | |||||||
|
State on delivery 3) |
Plugged (observe installation instructions) | |||||||
| 1) | Thread according to DIN 13 |
| 2) | The spot face can be deeper than specified in the appropriate standard. |
| 3) | Unless otherwise specified. Other layouts on request. |
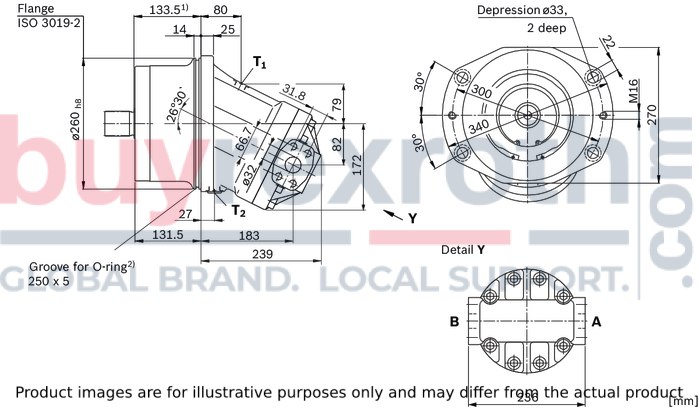
Size 250
| 1) | To shaft collar |
| 2) | The O-ring is not included in the delivery contents. |

| 1) | Center bore according to DIN 332 (thread according to DIN 13) |
Ports
|
Size |
250 | ||
|
A, B |
Working port |
Size |
1 1/4 in |
|
Standard |
Dimensions according to SAE J518 | ||
|
Fastening thread 1) |
M14 × 2; 19 mm deep | ||
|
State on delivery |
With protective cover (must be connected) | ||
|
T1 |
Drain port |
Size |
M22 × 1,5; 14 mm deep |
|
Standard 2) |
DIN 3852 | ||
|
State on delivery 3) |
With protective cover (observe installation instructions) | ||
|
T2 |
Drain port |
Size |
M22 × 1,5; 14 mm deep |
|
Standard 2) |
DIN 3852 | ||
|
State on delivery 3) |
Plugged (observe installation instructions) | ||
| 1) | Thread according to DIN 13 |
| 2) | The spot face can be deeper than specified in the appropriate standard. |
| 3) | Unless otherwise specified. Other layouts on request. |
Size 355
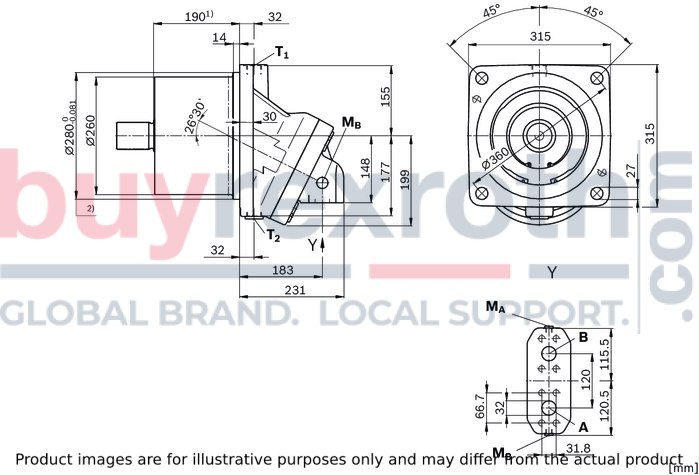
| 1) | To shaft collar |
| 2) | Flange ISO 3019-2 |

| 1) | Center bore according to DIN 332 (thread according to DIN 13) |
Ports
|
Size |
355 | ||
|
A, B |
Working port |
Size |
1 1/4 in |
|
Standard |
Dimensions according to SAE J518 | ||
|
Fastening thread 1) |
M14 × 2; 22 mm deep | ||
|
State on delivery |
With protective cover (must be connected) | ||
|
T1 |
Drain port |
Size |
M33 × 2; 18 mm deep |
|
Standard 2) |
DIN 3852 | ||
|
State on delivery 3) |
With protective cover (observe installation instructions) | ||
|
T2 |
Drain port |
Size |
M33 × 2; 18 mm deep |
|
Standard 2) |
DIN 3852 | ||
|
State on delivery 3) |
Plugged (observe installation instructions) | ||
|
MA, MB |
Measuring port pressure A, B |
Size |
M14 × 1,5; 12 mm deep |
|
Standard 2) |
DIN 3852 | ||
|
State on delivery |
Plugged | ||
| 1) | Thread according to DIN 13 |
| 2) | The spot face can be deeper than specified in the appropriate standard. |
| 3) | Unless otherwise specified. Other layouts on request. |
Flushing and boost pressure valve
The flushing and boost pressure valve is used in closed circuits for the removal of heat and to ensure a minimum boost pressure level.
Hydraulic fluid is directed from the respective low pressure side into the motor housing. This is then fed into the reservoir, together with the leakage. The removed hydraulic fluid must be replaced by cooled hydraulic fluid from the boost pump.
Cracking pressure of pressure retaining valve
(observe when setting the primary valve)
Sizes 45 to 355, fixed setting: 16 bar
Switching pressure of flushing piston Δp
Sizes 45 to 355: 8±1 bar
Flushing and boost pressure valve
The flushing and boost pressure valve is used in closed circuits for the removal of heat and to ensure a minimum boost pressure level.
Hydraulic fluid is directed from the respective low pressure side into the motor housing. This is then fed into the reservoir, together with the leakage. The removed hydraulic fluid must be replaced by cooled hydraulic fluid from the boost pump.
Cracking pressure of pressure retaining valve
(observe when setting the primary valve)
Sizes 45 to 355, fixed setting: 16 bar
Switching pressure of flushing piston Δp
Sizes 45 to 355: 8±1 bar
Circuit diagram

Circuit diagram

Flushing flow qv
Orifices (throttles with integrated valve) can be used to set the flushing flows as required.
The specifications below are based on:
ΔpND = pND – pG = 25 bar and ν = 10 mm²/s
(pND = low pressure, pG = case pressure)
Flushing flow qv
Orifices (throttles with integrated valve) can be used to set the flushing flows as required.
The specifications below are based on:
ΔpND = pND – pG = 25 bar and ν = 10 mm²/s
(pND = low pressure, pG = case pressure)
With sizes 45 to 180, orifices can be supplied for flushing flows from 3.5 to 10 l/min. For flushing flows deviating from the values in the table, please state the required flushing flow when ordering. The flushing flow without orifice is approx. 12 to 14 l/min at low pressure ΔpND = 25 bar.
With sizes 45 to 180, orifices can be supplied for flushing flows from 3.5 to 10 l/min. For flushing flows deviating from the values in the table, please state the required flushing flow when ordering. The flushing flow without orifice is approx. 12 to 14 l/min at low pressure ΔpND = 25 bar.
Dimensions
Dimensions
Port plate 027

Port plate 027

Port plate 107

Port plate 107

Pressure relief valve
The MHDB pressure relief valves protect the hydraulic motor from overload. As soon as the set cracking pressure is reached, the hydraulic fluid flows from the high-pressure side to the low-pressure side.
The pressure relief valves are only available in conjunction with connection plates 181, 191 or 192. (Connection plate 181: see section “BVD and BVE counterbalance valve”
Setting range of cracking pressure: 50 up to 420 bar
For versions “with pressure sequencing stage” (code 192), a higher pressure setting can be implemented by connecting an external pilot pressure of 25 up to 30 bar at port pSt.
When ordering, state in plain text:
Cracking pressure of pressure relief valve Cracking pressure with pilot pressure applied to pSt (only with version 192)Pressure relief valve
The MHDB pressure relief valves protect the hydraulic motor from overload. As soon as the set cracking pressure is reached, the hydraulic fluid flows from the high-pressure side to the low-pressure side.
The pressure relief valves are only available in conjunction with connection plates 181, 191 or 192. (Connection plate 181: see section “BVD and BVE counterbalance valve”
Setting range of cracking pressure: 50 up to 420 bar
For versions “with pressure sequencing stage” (code 192), a higher pressure setting can be implemented by connecting an external pilot pressure of 25 up to 30 bar at port pSt.
When ordering, state in plain text:
Cracking pressure of pressure relief valve Cracking pressure with pilot pressure applied to pSt (only with version 192)Version without pressure boost facility (code 191)
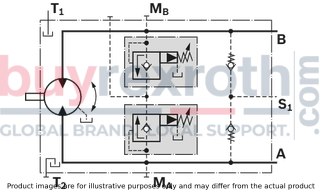
Version without pressure boost facility (code 191)

Version with pressure boost facility (code 192)
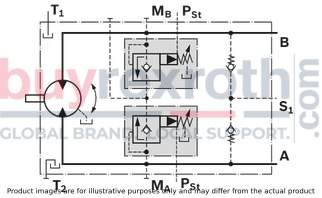
Version with pressure boost facility (code 192)

Dimensions
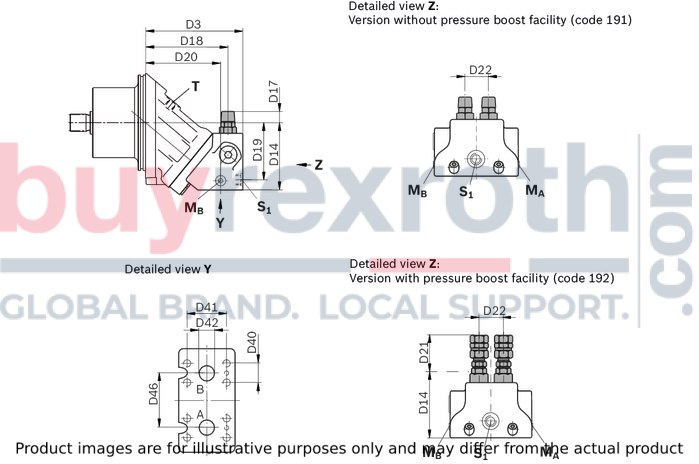
Dimensions

Counterbalance valve BVD and BVE
Function
Travel drive/winch counterbalance valves are designed to reduce the danger of overspeeding and cavitation of axial piston motors in open circuits. Cavitation occurs if the motor speed is greater than it should be for the given input flow while braking, travelling downhill, or lowering a load.
If the inlet pressure drops, the counterbalance spool throttles the return flow and brakes the motor until the inlet pressure returns to approx. 20 bar.
Note
BVD available for sizes 28 to 180 and BVE available for sizes 107 to 180. The counterbalance valve must be ordered additionally. We recommend ordering the counterbalance valve and the motor as a set. Ordering example: A2FM(E)90/61W–VAB188 + BVD20F27S/41B–V03K16D0400S12 The counterbalance valve does not replace the mechanical service brake and park brake. Observe the detailed notes on the BVD counterbalance valve in data sheet 95522 and BVE counterbalance valve in data sheet 95525! For the design of the brake release valve, we must know for the mechanical park brake: the pressure at the start of opening the volume of the counterbalance spool between minimum stroke (brake closed) and maximum stroke (brake released with 21 bar) the required closing time for a warm device (oil viscosity approx. 16 mm2/s)Travel drive counterbalance valve BVD...F
Application option:
Travel drive on wheeled excavatorsCounterbalance valve BVD and BVE
Function
Travel drive/winch counterbalance valves are designed to reduce the danger of overspeeding and cavitation of axial piston motors in open circuits. Cavitation occurs if the motor speed is greater than it should be for the given input flow while braking, travelling downhill, or lowering a load.
If the inlet pressure drops, the counterbalance spool throttles the return flow and brakes the motor until the inlet pressure returns to approx. 20 bar.
Note
BVD available for sizes 28 to 180 and BVE available for sizes 107 to 180. The counterbalance valve must be ordered additionally. We recommend ordering the counterbalance valve and the motor as a set. Ordering example: A2FM(E)90/61W–VAB188 + BVD20F27S/41B–V03K16D0400S12 The counterbalance valve does not replace the mechanical service brake and park brake. Observe the detailed notes on the BVD counterbalance valve in data sheet 95522 and BVE counterbalance valve in data sheet 95525! For the design of the brake release valve, we must know for the mechanical park brake: the pressure at the start of opening the volume of the counterbalance spool between minimum stroke (brake closed) and maximum stroke (brake released with 21 bar) the required closing time for a warm device (oil viscosity approx. 16 mm2/s)Travel drive counterbalance valve BVD...F
Application option:
Travel drive on wheeled excavatorsExample schematic for travel drive on wheeled excavators
A2FM(E)090/61W-VAB188 + BVD20F27S/41B–V03K16D0400S12
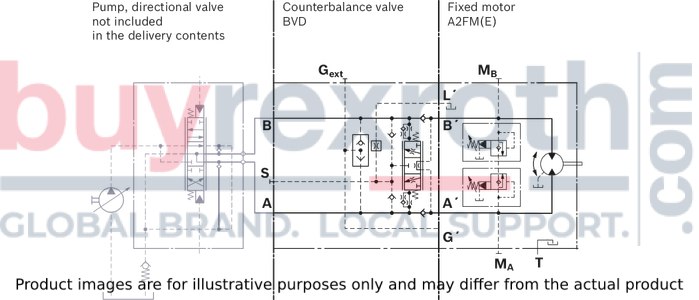
Example schematic for travel drive on wheeled excavators
A2FM(E)090/61W-VAB188 + BVD20F27S/41B–V03K16D0400S12

Winch counterbalance valve BVD...W and BVE
Application options:
Winch drive in cranes (BVD and BVE) Track drive in excavator crawlers (BVD)Winch counterbalance valve BVD...W and BVE
Application options:
Winch drive in cranes (BVD and BVE) Track drive in excavator crawlers (BVD)
Example schematic for winch drive in cranes
A2FM(E)090/61W-VAB188 + BVE25W385/51ND-V100K00D4599T30S00-0
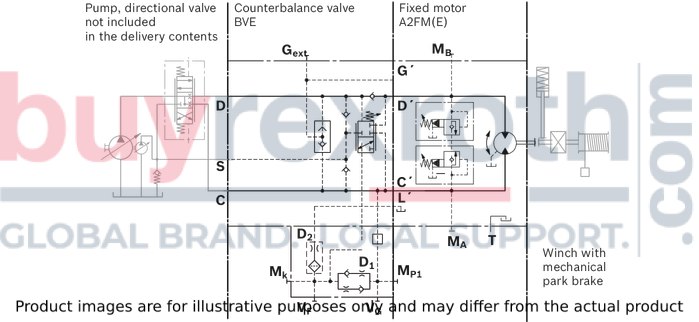
Example schematic for winch drive in cranes
A2FM(E)090/61W-VAB188 + BVE25W385/51ND-V100K00D4599T30S00-0



Speed sensors
The versions A2FE...U and A2FE...F ("prepared for speed sensor", i.e. without sensor) are equipped with a toothed ring on the rotary group.
On deliveries "prepared for speed sensor", the port is plugged with a pressure-resistant cover.
With the DSA or HDD speed sensor mounted a signal proportional to motor speed can be generated. The sensors measures the speed and direction of rotation.
Ordering code, technical data, dimensions and details on the connector, plus safety information about the sensor can be found in the relevant data sheet.
DSA: data sheet 95133
HDD: data sheet 95135
The sensor is mounted at the specially provided port as follows:
DSA: with one mounting bolt
HDD: with two mounting bolts
We recommend ordering the A2FE plug-in motor complete with sensor mounted.
Speed sensors
The versions A2FE...U and A2FE...F ("prepared for speed sensor", i.e. without sensor) are equipped with a toothed ring on the rotary group.
On deliveries "prepared for speed sensor", the port is plugged with a pressure-resistant cover.
With the DSA or HDD speed sensor mounted a signal proportional to motor speed can be generated. The sensors measures the speed and direction of rotation.
Ordering code, technical data, dimensions and details on the connector, plus safety information about the sensor can be found in the relevant data sheet.
DSA: data sheet 95133
HDD: data sheet 95135
The sensor is mounted at the specially provided port as follows:
DSA: with one mounting bolt
HDD: with two mounting bolts
We recommend ordering the A2FE plug-in motor complete with sensor mounted.
DSA speed sensor mounted (code V)
Size 28 … 250
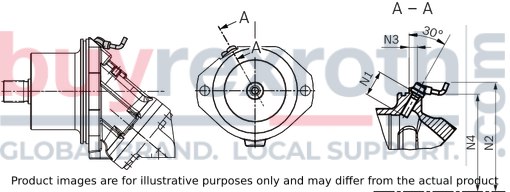
DSA speed sensor mounted (code V)
Size 28 … 250

HDD speed sensor mounted (code H)
Size 63 … 180
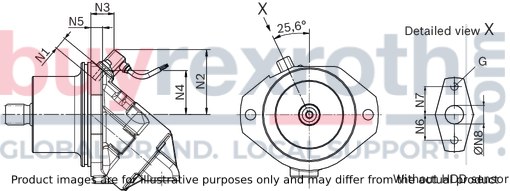
HDD speed sensor mounted (code H)
Size 63 … 180

Installation instructions
General
During commissioning and operation, the axial piston unit must be filled with hydraulic fluid and air bled. This must also be observed following a relatively long standstill as the axial piston unit may drain back to the reservoir via the hydraulic lines. The case drain fluid in the housing must be directed to the reservoir via the highest available drain port (T1,T2). If a shared drain line is used for several units, make sure that the respective case pressure is not exceeded. The shared drain line must be dimensioned to ensure that the maximum permissible case pressure of all connected units is not exceeded in any operating conditions, specifically on cold start. If this is not possible, separate reservoir lines must be laid as required. To achieve favorable noise values, all connecting lines should be decoupled by using elastic elements and above-reservoir installation is to be avoided. In all operating conditions, the drain line must flow into the reservoir below the minimum fluid level.Installation position
See the following examples 1 to 6.
Further installation positions are possible upon request. Recommended installation position: 1 and 2.
Below-tank installation (standard)
Below-tank installation is at hand if the axial piston unit is installed below the minimum liquid level outside the tank.
| 1) | Standard for sizes 250 and 355, special version for sizes 28 to 180. |
| 2) | Piping suggestion without port T2 (sizes 28 to 180) |
| 3) | Piping suggestion with Port T2 (sizes 250 to 355). |
Above-reservoir installation
Above-reservoir installation means that the axial piston unit is installed above the minimum fluid level of the reservoir.
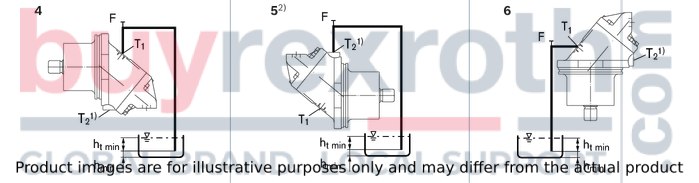
| 1) | Standard for sizes 250 and 355, special version for sizes 28 to 180. |
| 2) | Installation position only permissible if port T2 is fitted (sizes 250 and 355). |
|
Installation position |
Air bleeding |
Filling |
|
1 |
‒ |
T1 |
|
2 |
‒ |
T1 (NG28 bis 180) T2 (NG250 und 355) |
|
3 |
‒ |
T1 |
|
4 |
(F) |
T1, (F) |
|
5 |
(F) |
T2, (F) |
|
6 |
(F) |
T1, (F) |
|
Key |
|
|
F |
Filling / Air bleeding |
|
T1, T2 |
Suction port |
|
ht min |
Minimum required immersion depth (200 mm) |
|
hmin |
Minimum required spacing to reservoir bottom (100 mm) |
Note
Connection F is part of the external piping and must be provided on the customer side to simplify the filling and bleeding.General project planning notes
The axial piston unit is designed to be used in open and closed circuits. The project planning, installation and commissioning of the axial piston unit require the involvement of qualified skilled personnel. Before using the axial piston unit, please read the corresponding instruction manual completely and thoroughly. If necessary, request it from Bosch Rexroth. Before finalizing your design, request a binding installation drawing. The specified datas and notes must be observed. Preservation: Our axial piston units are supplied as standard with preservative protection for a maximum of 12 months. If longer preservative protection is required (maximum 24 months), please specify this in plain text when placing your order. The preservation times are valid under optimal storage conditions. Details of these conditions can be found in the data sheet 90312 or the instruction manual. Not all versions of the product are approved for use in a safety function according to ISO 13849. Please consult the responsible contact person at Bosch Rexroth if you require reliability parameters (e.g. MTTFD) for functional safety. A pressure relief valve is to be provided in the hydraulic system. Observe the instructions in the instruction manual regarding tightening torques of connection threads and other threaded joints used. The notes in the instruction manual on tightening torques of the port threads and other screw joints must be observed. The ports and fastening threads are designed for the permissible maximum pressure pmax (see instruction manual). The machine or system manufacturer must ensure that the connecting elements and lines correspond to the specified operating conditions (pressure, flow, hydraulic fluid, temperature) with the necessary safety factors. The working ports and function ports are designated only to accommodate hydraulic lines.Counterbalance valve
BVD 20-25

Counterbalance valve
BVD 20-25
Double acting for travel drives and winch drives Size 20 … 25 Nominal pressure 350 bar Maximum pressure 420 bar Direct attachment on Rexroth axial piston motors (A2FM / A2FE / A6VM / A6VE)Data sheet
Counterbalance valve
BVD 20-25

Counterbalance valve
BVD 20-25
Double acting for travel drives and winch drives Size 20 … 25 Nominal pressure 350 bar Maximum pressure 420 bar Direct attachment on Rexroth axial piston motors (A2FM / A2FE / A6VM / A6VE)Data sheet
Counterbalance valve
BVD 20-25

Counterbalance valve
BVD 20-25
Double acting for travel drives and winch drives Size 20 … 25 Nominal pressure 350 bar Maximum pressure 420 bar Direct attachment on Rexroth axial piston motors (A2FM / A2FE / A6VM / A6VE)Data sheet
Counterbalance valve
BVE 25

Counterbalance valve
BVE 25
Single acting for controlled load lowering in winch drives Size 25 Nominal pressure pump side 350 bar Nominal pressure motor side 420 bar Direct attachment on Rexroth axial piston motors (A2FM / A2FE / A6VM / A6VE)Data sheet
Counterbalance valve
BVD 20-25

Counterbalance valve
BVD 20-25
Double acting for travel drives and winch drives Size 20 … 25 Nominal pressure 350 bar Maximum pressure 420 bar Direct attachment on Rexroth axial piston motors (A2FM / A2FE / A6VM / A6VE)Data sheet
Counterbalance valve
BVE 25

Counterbalance valve
BVE 25
Single acting for controlled load lowering in winch drives Size 25 Nominal pressure pump side 350 bar Nominal pressure motor side 420 bar Direct attachment on Rexroth axial piston motors (A2FM / A2FE / A6VM / A6VE)Data sheet
Counterbalance valve
BVD 20-25

Counterbalance valve
BVD 20-25
Double acting for travel drives and winch drives Size 20 … 25 Nominal pressure 350 bar Maximum pressure 420 bar Direct attachment on Rexroth axial piston motors (A2FM / A2FE / A6VM / A6VE)Data sheet
Counterbalance valve
BVE 25

Counterbalance valve
BVE 25
Single acting for controlled load lowering in winch drives Size 25 Nominal pressure pump side 350 bar Nominal pressure motor side 420 bar Direct attachment on Rexroth axial piston motors (A2FM / A2FE / A6VM / A6VE)Data sheet
Counterbalance valve
BVD 20-25

Counterbalance valve
BVD 20-25
Double acting for travel drives and winch drives Size 20 … 25 Nominal pressure 350 bar Maximum pressure 420 bar Direct attachment on Rexroth axial piston motors (A2FM / A2FE / A6VM / A6VE)Data sheet
Counterbalance valve
BVE 25

Counterbalance valve
BVE 25
Single acting for controlled load lowering in winch drives Size 25 Nominal pressure pump side 350 bar Nominal pressure motor side 420 bar Direct attachment on Rexroth axial piston motors (A2FM / A2FE / A6VM / A6VE)Data sheet
During and shortly after operation, there is a risk of burns on the axial piston unit. Take appropriate safety measures (e.g. by wearing protective clothing).
Related Products
R902232895
$3,611.00 USD
R902249850
$13,318.00 USD
R902156283
$7,467.00 USD
R902469283
$24,817.00 USD
R902130728
$11,633.00 USD








