***Disclaimer: The following summary contains information gathered from various sources such as product descriptions, technical specifications and catalogs. While efforts have been made to provide accurate details, inaccuracies may occur. It is advised to verify all information by contacting Bosch Rexroth directly.***
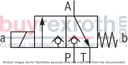
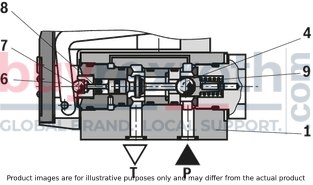
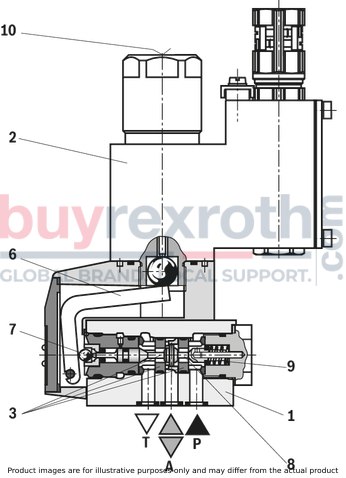
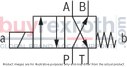
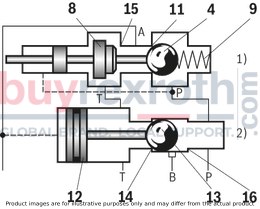
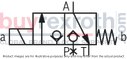
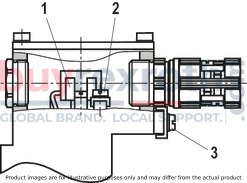
The Bosch Rexroth M-3SEW6C3X/420MW110RN9XEZ2/V (R901067845) is a high-performance directional seat valve designed for controlling the start, stop, and direction of fluid flow in hydraulic systems. This direct-operated valve features solenoid actuation and is constructed with a durable housing, a robust solenoid, a hardened valve system, and a precision control spool. The control spool is pressure-compensated between two sealing elements connected to port P, ensuring reliable operation even under varying pressure conditions.
This particular model is equipped with a negative spool overlap where port T must always be connected. This design allows for quick switching between ports during operation without significant impact on most applications. Additionally, the valve includes a manual override for activation without solenoid energization.
The M-3SEW6C3X/420MW110RN9XEZ2/V valve offers various configurations including initial and spool positions for different operational requirements. It also supports the use of throttle and check valve inserts to manage flow rates and prevent backflow respectively. These inserts can be placed into port P of either the seat valve or an additional Plus plate for enhanced functionality.
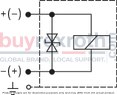
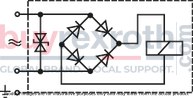
Designed to accommodate multiple applications, this Bosch Rexroth directional seat valve can be used in potentially explosive atmospheres. It adheres to ISO porting patterns (excluding locating hole) and ensures safe switching even after extended periods under pressure. The airgap DC and AC solenoids enhance safety further by preventing electrical malfunctions. The solenoid coil can be rotated by 90 degrees for flexible installation, while electrical connections are facilitated through individual connections and cable glands. An optional concealed manual override feature adds to the versatility of this hydraulic component.
In summary, the Bosch Rexroth M-3SEW6C3X/420MW110RN9XEZ2/V directional seat valve stands out as a reliable choice for precise control over hydraulic flow in complex systems while maintaining safety standards suitable for challenging environments.
$4,369.00 USD
More are expected on September 16, 2026
Note: Sales tax, shipping, and applicable tariffs will be calculated at checkout.Status: This product is temporarily out of stock.
Qty: Delivered as early as September 16, 2026 when ordered in